Inclusive education has become a cornerstone of modern educational systems. At A Heart 2 Help, we recognize the importance of understanding the legal framework that supports this approach.
Related legislations and policies that support inclusive education include several key acts that have shaped the educational landscape. These laws have not only increased access to general education classrooms but also improved outcomes for students with disabilities.
Key Laws Shaping Inclusive Education
The landscape of inclusive education in the United States has undergone significant transformation due to several landmark pieces of legislation. These laws have revolutionized the approach to education for students with disabilities, ensuring their right to equal educational opportunities.
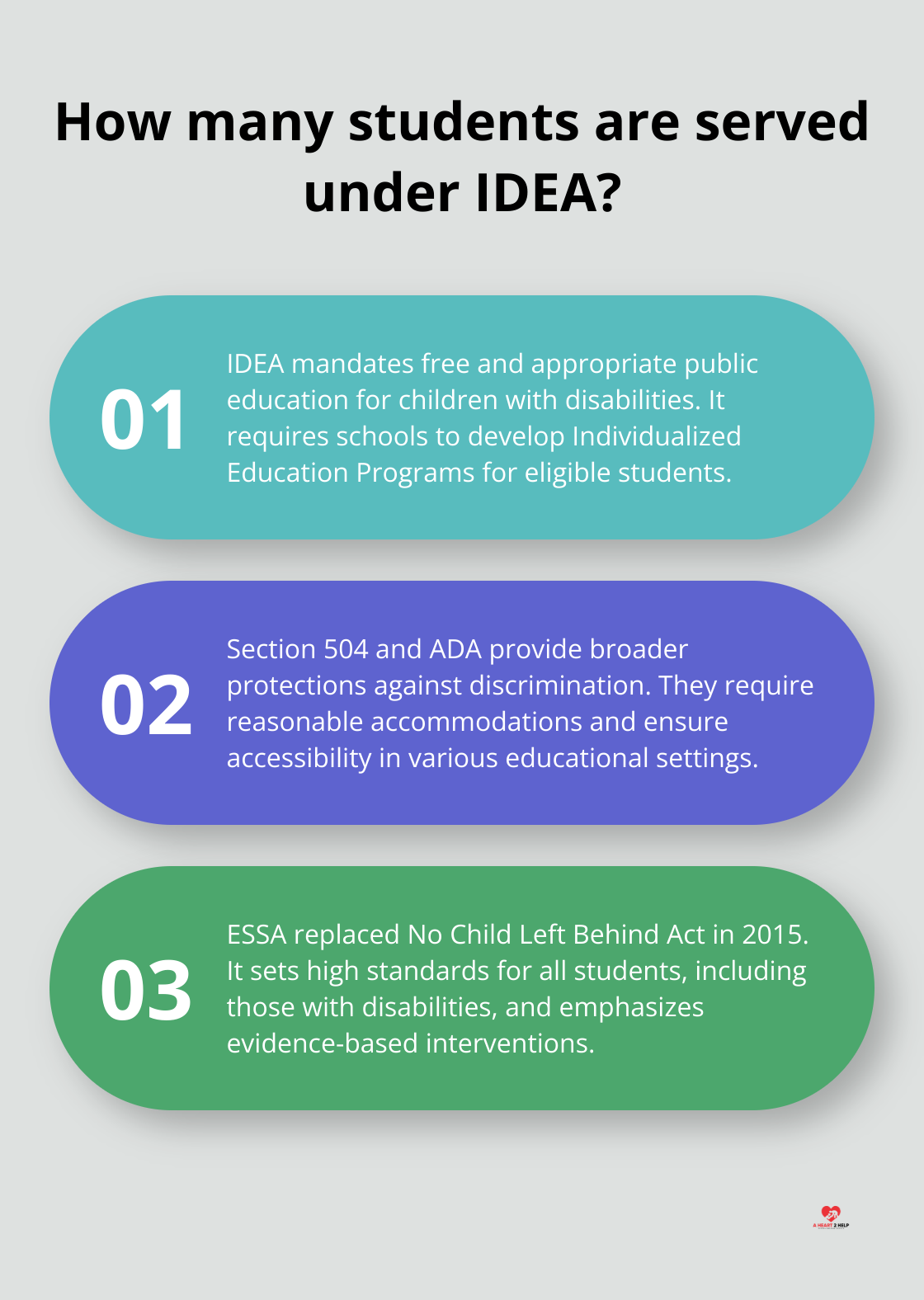
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
IDEA stands as the foundation of special education law in the U.S. Enacted in 1990 and reauthorized in 2004, this federal law mandates that all children with disabilities receive a free and appropriate public education (FAPE) in the least restrictive environment. The law requires schools to develop Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) for each eligible student, tailoring education to their specific needs.
Section 504 and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
While IDEA focuses specifically on special education, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and the ADA of 1990 provide broader protections against discrimination. Section 504 applies to all federally funded programs (including public schools) and requires reasonable accommodations for students with disabilities. The ADA extends these protections to private schools and other public accommodations, ensuring accessibility and equal opportunities across various settings.
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
Signed into law in 2015, ESSA replaced the No Child Left Behind Act and reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act. While not exclusively focused on students with disabilities, ESSA includes provisions that support inclusive education. It requires states to set high standards for all students, including those with disabilities, and to provide appropriate accommodations in assessments. ESSA also emphasizes the importance of evidence-based interventions and supports for struggling students.
Impact of Inclusive Education Laws
The combined impact of these laws has been substantial. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, the number of students ages 3–21 served under IDEA in the United States increased from 6.4 million in school year 2012–13 to 7.5 million in school year 2022–23. This shift towards inclusion not only benefits students with disabilities but also fosters a more diverse and understanding learning environment for all students.
Ongoing Challenges
Despite the progress made, challenges persist in fully implementing these laws. Funding constraints, the need for ongoing teacher training, and the complexity of balancing individual needs with classroom dynamics continue to present obstacles. These challenges underscore the importance of continued advocacy and support for inclusive education practices.
As we move forward, it becomes essential to examine the real-world impact of these legislative efforts on students, educators, and the broader educational landscape.
How Inclusive Education Legislation Has Transformed Schools
Increased Presence in General Education Classrooms
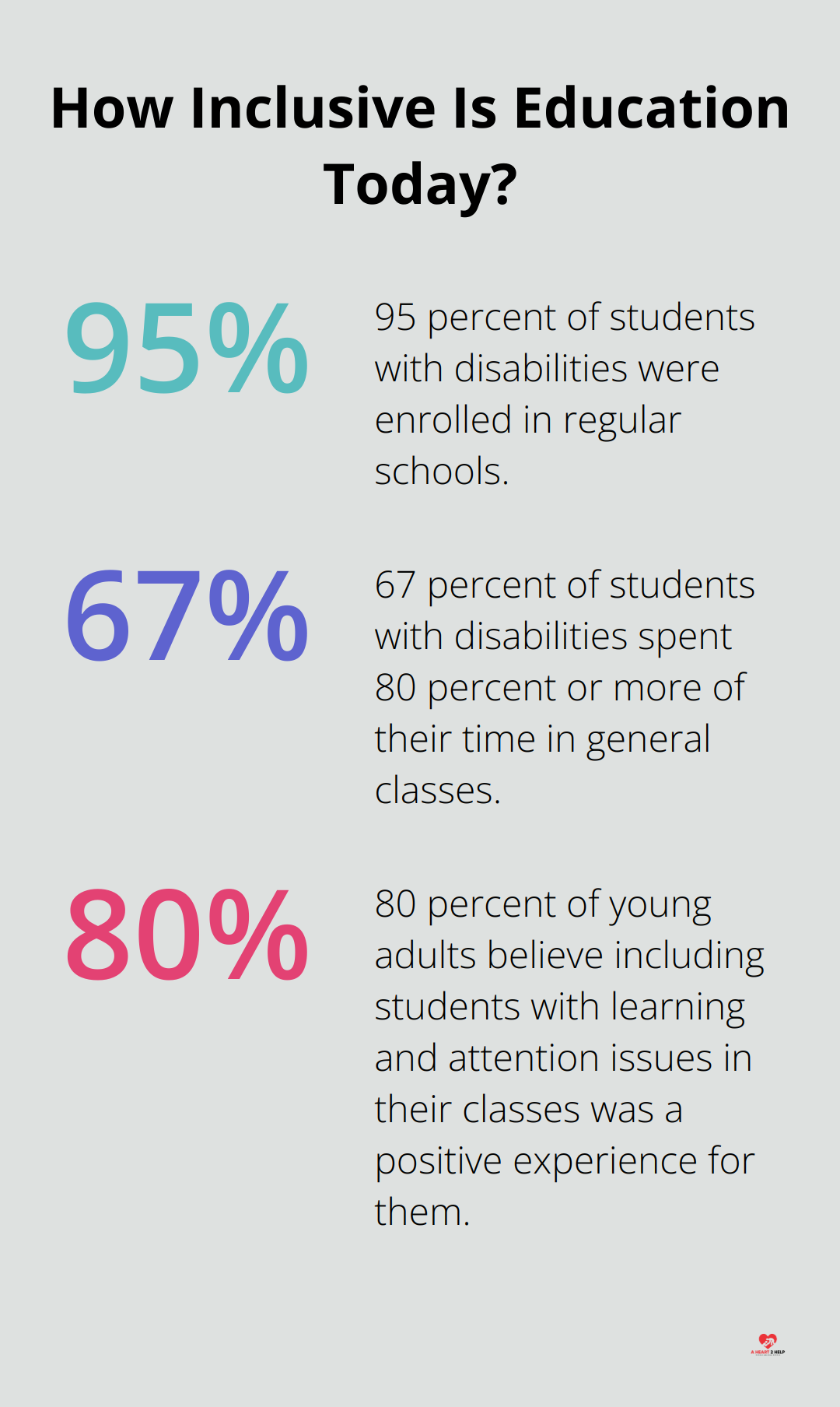
The implementation of inclusive education legislation has led to a significant increase in students with disabilities spending time in general education classrooms. 95 percent were enrolled in regular schools, and the percentage who spent 80 percent or more of their time in general classes increased from 61 to 67 percent. This reflects a growing commitment to inclusive practices.
Improved Academic Outcomes
Inclusive education has resulted in improved academic outcomes for many students with disabilities. A study published in the Journal of Special Education found that students with disabilities who spent more time in general education classrooms showed higher rates of progress in reading and math compared to their peers in more segregated settings. This progress extends beyond academics; many students with disabilities in inclusive settings also demonstrate improved communication skills and adaptive behaviors.
Enhanced Social Integration
The social impact of inclusive education is profound. When students with and without disabilities learn side by side, it fosters understanding and acceptance. The National Center on Educational Outcomes focuses on the inclusion of students with disabilities, English learners, and English learners with disabilities. These experiences prepare all students for a diverse society.
Reduced Stigma and Discrimination
One of the most significant impacts of inclusive education legislation has been the gradual shift in societal attitudes towards disability. As more students with disabilities participate in general education settings, we observe a reduction in stigma and discrimination. A survey by the National Center for Learning Disabilities found that 80% of young adults believe including students with learning and attention issues in their classes was a positive experience for them.
Ongoing Challenges and Future Directions
While progress has been made, obstacles remain in fully realizing the promise of inclusive education. Funding constraints, the need for ongoing teacher training, and the complexity of balancing individual needs with classroom dynamics continue to present challenges. These issues highlight the importance of continued advocacy and support for inclusive education practices (which are essential for creating truly equitable learning environments).
As we move forward, it’s important to address these challenges head-on. The next section will explore the specific hurdles that schools, educators, and policymakers face in implementing inclusive education laws, and discuss potential strategies for overcoming these barriers.
Overcoming Hurdles in Inclusive Education
Implementing inclusive education laws presents significant challenges for schools and educators. Let’s explore some of the major obstacles and potential solutions.
Financial Constraints and Resource Allocation
One of the biggest hurdles in implementing inclusive education is funding. The IDEA is a grants statute that provides federal funding for the education of children with disabilities and requires, as a condition for the receipt of such funding, that states agree to provide a free appropriate public education (FAPE) to eligible children with disabilities. However, the federal government has never fully funded IDEA to the level initially promised.

This funding gap directly impacts the quality of inclusive education. Schools struggle to provide necessary resources (such as assistive technologies, specialized instructional materials, and additional support staff). Some districts have found success in pooling resources across schools or partnering with local businesses and organizations to supplement their budgets.
Inadequate Teacher Preparation
Many general education teachers feel unprepared to meet the diverse needs of students with disabilities in inclusive classrooms. Research indicates that special education teachers rate themselves as more prepared for both instruction and social inclusion of students with disabilities than general education teachers.
To tackle this issue, schools need to invest in comprehensive professional development programs. Some effective approaches include:
- Ongoing, job-embedded training rather than one-off workshops
- Collaborative teaching models where special and general educators work together
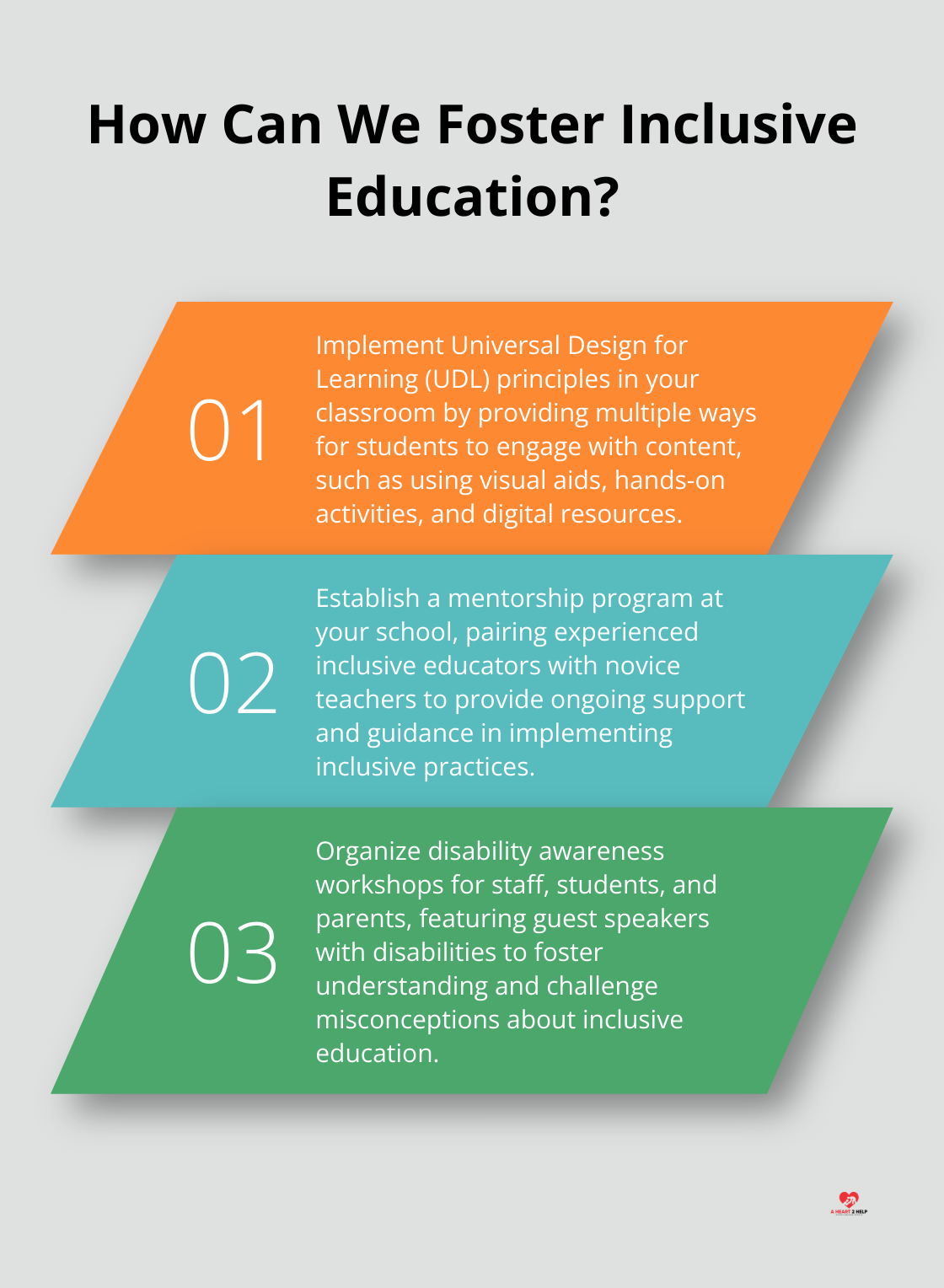
- Mentorship programs pairing experienced inclusive educators with novices
Balancing Diverse Needs in the Classroom
Creating a learning environment that meets the needs of all students, with and without disabilities, is a complex task. Teachers often struggle to differentiate instruction effectively while maintaining high standards for all learners.
Successful inclusive classrooms often utilize Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles. This framework provides flexibility in how information is presented, how students demonstrate knowledge, and how they are engaged in learning. Teachers can better accommodate diverse learning needs without compromising educational quality by designing lessons with multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement.
Shifting Mindsets and Overcoming Bias
The most challenging aspect of implementing inclusive education is overcoming attitudinal barriers. Misconceptions about disabilities and low expectations for students with special needs can hinder progress.
Education and exposure are key to changing these attitudes. Schools that have successfully fostered inclusive cultures often implement awareness programs for staff, students, and parents. These might include disability awareness workshops, guest speakers with disabilities, or inclusive extracurricular activities (which promote understanding and acceptance).
Overcoming these hurdles requires a community access support approach, involving all stakeholders in the educational process to create truly inclusive learning environments.
Final Thoughts
Inclusive education laws have transformed the educational landscape, increasing accessibility and equity for students with disabilities. These related legislations and policies that support inclusive education include IDEA, ADA, and ESSA, which have improved outcomes and classroom integration. However, challenges persist in funding, teacher preparation, and balancing diverse needs within classrooms.
The future of inclusive education requires continued advocacy and improvement of existing legislation. Full funding for special education programs, comprehensive teacher training, and fostering a culture of acceptance in schools and communities remain critical goals. At A Heart 2 Help, we believe in the power of community support to drive positive change.
Our innovative care-app connects those who need assistance with compassionate volunteers, extending inclusivity beyond the classroom. We encourage everyone to support inclusive practices, empower educators, and work to break down barriers for all students. This collective effort will create an educational system that serves every learner, preparing them for success in school and beyond.

